The e-commerce industry is experiencing rapid transformations, and the next generation of the internet, Web 3.0, is poised to revolutionize it even further. It promises a more intelligent, decentralized, and secure online environment by integrating artificial intelligence, blockchain, and the Internet of Things (IoT). With this new paradigm, users will gain greater control over their data, leading to quicker and safer transactions.
Web 3.0 technology will significantly impact how businesses engage with customers in the e-commerce sector, fundamentally altering the landscape of online retail. Embracing Web 3.0 in retail operations is of utmost importance, given that the market for this technology is projected to soar from $6.8 billion in 2020 to a staggering $48.3 billion by 2025.
Evolution of Web
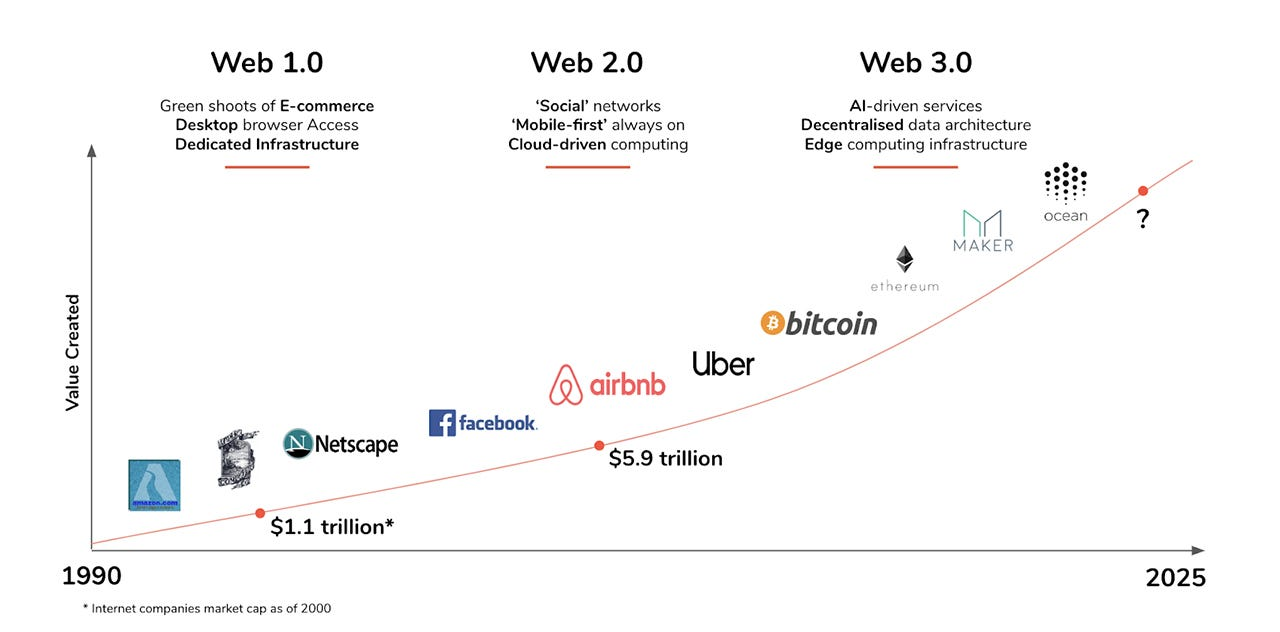
Web 1.0, also known as the birth of the World Wide Web (WWW), marked a revolutionary era in the previous century from 1990 to 2000. Pioneering companies like Amazon, Apple, and Netscape were among the early adopters. During this period, websites primarily consisted of static web pages, with content retrieved from the server’s file system.
Web 1.0 was centered around reading, whereas Web 2.0 shifted its focus towards user participation and contribution. The advent of interactive web pages opened the doors to user-generated content. Web 2.0 introduced dynamic content that responded to users\’ inputs, enabling actions such as commenting on pages, sharing photos on platforms, creating communities, and much more.
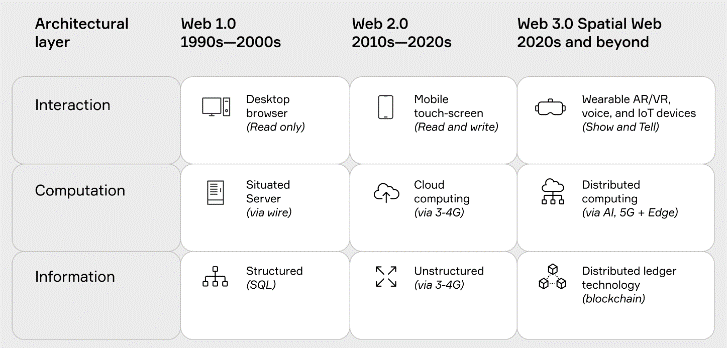
The proliferation of mobile Internet access and the emergence of social networks have significantly fueled the growth of Web 2.0. This phase encourages individual expression and facilitates various forms of interaction, such as podcasting, social media, tagging, blogging, commenting, social networking, and web content voting.
Web 3.0 brings a paradigm shift by focusing on the concepts of reading, writing, and ownership. Now, builders and creators could own a stake in their own community through NFTs, tokens, and similar mechanisms.
The Importance of Web 3.0
- In the era of web 2.0, tech giants like Google and Amazon capitalized on customer data, but web 3.0’s global peer-to-peer network aims to curb data hoarding without proper consent.
- Web 3.0 serves as the foundation for the metaverse, an envisioned 3D virtual world where individuals interact and conduct business through digital avatars.
- The enhanced transparency offered by immutable blockchain ledgers could revolutionize customer service by granting both parties access to their transaction records.
- Web 3.0’s marketing capabilities enable tailored products and services for individuals, potentially striking a better balance between privacy and personalization compared to the current web.
How is it going to Change Retail Industry
Web 1.0 offered limited opportunities for the retail industry, but everything changed with the advent of Web 2.0. Two-way communication, apps, and social media made shopping easier, while personalization brought a customer-centric approach. Now, with the emergence of Web 3.0, even more possibilities arise.
Web 3.0 ushers in a new era of heightened personalization, granting customers greater control over their data and promoting decentralization. Customers will gain precise information about their transactions, enjoying real-time visibility on their order statuses.
Small businesses can benefit from creative and affordable marketing alternatives, and local companies can directly engage customers through relevant content.
The networked and machine-processable data of Web 3.0 leads to more effective and safer supply chain management, driving down costs and elevating the quality of goods and services due to its decentralized structure.
The main attractions are:
Metaverse
In the metaverse of Web 3.0, shoppers engage with unique, custom avatars represented as NFTs. These avatars explore the immersive 3D virtual space, visiting various stores and experiencing products firsthand. The metaverse addresses five crucial buyer needs: Context, Commerce, Content, Community, and Personalized vertical search.
Social Commerce
Consumers can connect with each other and with sellers, sharing product recommendations, reviews, and other information. Additionally, consumers can use cryptocurrency to make purchases on social commerce platforms or earn tokens and other rewards for sharing product recommendations or engaging in other activities.

Data risks in Web 3.0
Issue 1. Reliability of information
Decentralization in Web 3.0 gives rise to concerns regarding the authenticity and originality of information. Several unanswered questions arise, such as: How will the security and accuracy checks be implemented?, Who will be responsible for validating the data and How can data manipulation be detected and prevented?
Issue 2. Data availability
Excessive reliance on data by users poses challenges in predicting the behavior of built systems and the potential consequences if the data becomes inaccessible. Moreover, the network can face issues if one or two nodes fail, affecting the entire system.
Issue 3. Data security
Blockchain, known for its robust encryption, is considered one of the most secure technologies. However, hackers have discovered vulnerabilities like 51% attacks, Sybil attacks, phishing attacks, and theft of user keys, undermining the seemingly solid system.
Issue 4. User authentication and signature
Most apps do not authenticate or sign responses to user requests. Consequently, when a user’s digital wallet receives data from such apps, it becomes challenging to verify the authenticity of the response and determine whether it originates from a legitimate app or not
Future of eCommerce with Web 3.0
Web 3.0 is set to redefine the future of e-commerce, offering a more interconnected, customer-focused, and secure online retail landscape. To embrace this transformation, businesses must proactively invest in blockchain technology, artificial intelligence, and machine learning algorithms.
By doing so, they can gain a competitive edge and capitalize on the unlimited opportunities that Web 3.0 brings. The potential revolution in the e-commerce industry is both exciting and promising, and taking the lead in this paradigm shift is a thrilling prospect for companies.
